1주: 물질과 힘 그리고 측정(Matter and forces, measuring and counting)
W1.0 환영(Welcome)
W1.1 물질(Matter)
W1.2 힘(Forces)
W1.2a 자연단위(Natural units)
W1.2b 특수 상대론과 4-벡터(Special relativity and four-vector)
W1.2c 가상입자(Virtual Particles)
W1.3 확률과 단면(Probability and cross section)
W1.3a 광자 빔의 감쇄(Attenuation of a photon beam)/동영상/영문자막/슬라이드

광자 빔이 납 판을 통 동과하며 일어나는 감쇄를 계산 해봄으로써 단면과 확률의 관계를 알아보기로 한다. 이 계산의 결과는 상당히 의외의 결과가 나온다.
We calculate the attenuation of a photon beam of energy 1 MeV by a one centimeter thick lead plate.
The attenuation of the beam intensity I is exponential with three factors in the exponent:
- the cross section σ between photons and lead nuclei
- the density ρ of target nuclei
- the thickness ∆x of the target

Let us first consider lead properties.
- mass density is about 10,000 kilograms per cubic meter. The molecular weight is 0.20 kilogram per mole and the number of nuclei per mole is given by Avogadro's number.
- the cross section between 1 MeV photons and lead nuclei. We get it from the data collected by the Particle Data Group. And 1 MeV we find a huge cross section of about 10 barns.
With this we can calculate the attenuation of the beam.
First, the number density of lead nuclei is approximately 3 times 10^28 per cubic meter.
The exponent of the attenuation law is thus of the order of 0.33. That is to say that the beam is attenuated by only about 28%. There is no less than 72% of the beam which passes this one centimeter thick lead plate, despite the enormous cross section.
감쇄는 지수 함수로 일어난다. 1MeV의 광자가 두께 1cm의 납판(lead sheet)을 통과 할 때 약 28%의 감쇄가 있을 뿐이다. 단면이 엄청 큼에도 약 78% 가량의 광자는 그냥 통과해 버린다.
* 납판으로 (방사성)입자(전자기파)를 막으려면 엄청난 두께의 납으로된 방호벽이 필요하다. 빛을 가리는 것은 아주 극히 일부 영역의 가시광을 차단했을 뿐이다. 고에너지 전자기파는 두꺼운 철판도 통과한다. 원자력 발전소 원자로 내부 압력용기의 철판 두께는 23cm, 외부 콘크리트(고에너지 방사선 차단 효과는 없겠지만) 두께 1.2m
* Radiation
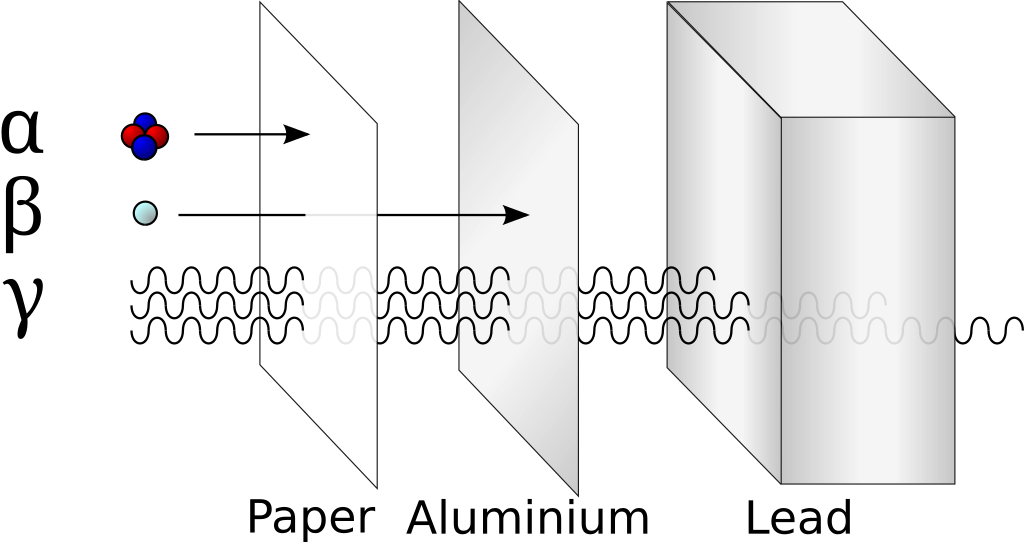
* 납판으로 (방사성)입자(전자기파)를 막으려면 엄청난 두께의 납으로된 방호벽이 필요하다. 빛을 가리는 것은 아주 극히 일부 영역의 가시광을 차단했을 뿐이다. 고에너지 전자기파는 두꺼운 철판도 통과한다. 원자력 발전소 원자로 내부 압력용기의 철판 두께는 23cm, 외부 콘크리트(고에너지 방사선 차단 효과는 없겠지만) 두께 1.2m
* Radiation



댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기